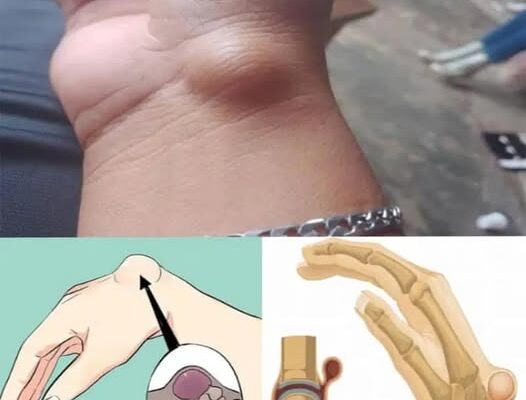
A wrist ganglion, also known as a synovial cyst, is a fluid-filled lump that commonly appears on the back or front of the wrist. It is a benign condition, but it can cause discomfort or interfere with joint movement.Why does a wrist ganglion appear?A wrist ganglion forms when synovial fluid, which lubricates the joints and tendons, accumulates in an abnormal capsule or bursa. Although there is not always a clear cause, some factors may influence its appearance: Repetitive use of the wrist: Activities such as writing, typing, or playing sports can put stress on the joint. Previous injuries: A blow or sprain to the wrist can trigger the cyst’s formation. Arthritis: In some cases, osteoarthritis may be linked to the appearance of ganglions.Genetic factors: Some people have a hereditary predisposition to developing these cysts.Wrist Ganglion SymptomsSynovial cysts vary in size and can grow or shrink over time. Symptoms include: A visible, soft lump on the wrist.Pain or discomfort when moving the joint.A feeling of pressure or numbness if the ganglion presses on a nerve.Wrist Ganglion TreatmentsTreatment depends on the size of the cyst and whether it causes pain or limits movement. Some options include:1. ObservationIf the ganglion is not painful or affecting mobility, doctors usually recommend doing nothing and just observing if it goes away on its own.2. ImmobilizationWearing a splint or wrist brace can reduce pressure on the joint and prevent the cyst from growing.3. Aspiration A doctor can drain the fluid with a needle, but there is a chance the cyst could recur.4. SurgeryIf the ganglion causes severe pain or limits mobility, it can be removed surgically. This procedure has a lower chance of recurrence.ConclusionA wrist ganglion is a benign condition, but if it causes discomfort, several treatments are available. Consulting a doctor is essential to determine the best option for each case.

